This year’s El Niño may drive ocean temperatures to “substantially exceed” those recorded during the last strong event in early 2016, scientists have warned.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) latest El Niño update also says there is a more than 95% chance the event will last through to February 2024, with far-reaching climate impacts.
“El Niño is anticipated to continue through the Northern Hemisphere winter,” NOAA staff wrote in the update. “Our global climate models are predicting that the warmer-than-average Pacific ocean conditions will not only last through the winter, but continue to increase.”
Scientists officially announced the onset of El Niño in early June. El Niño is an ocean-warming event that typically occurs every two to seven years in the central and eastern Pacific, driving air temperatures up around the globe.
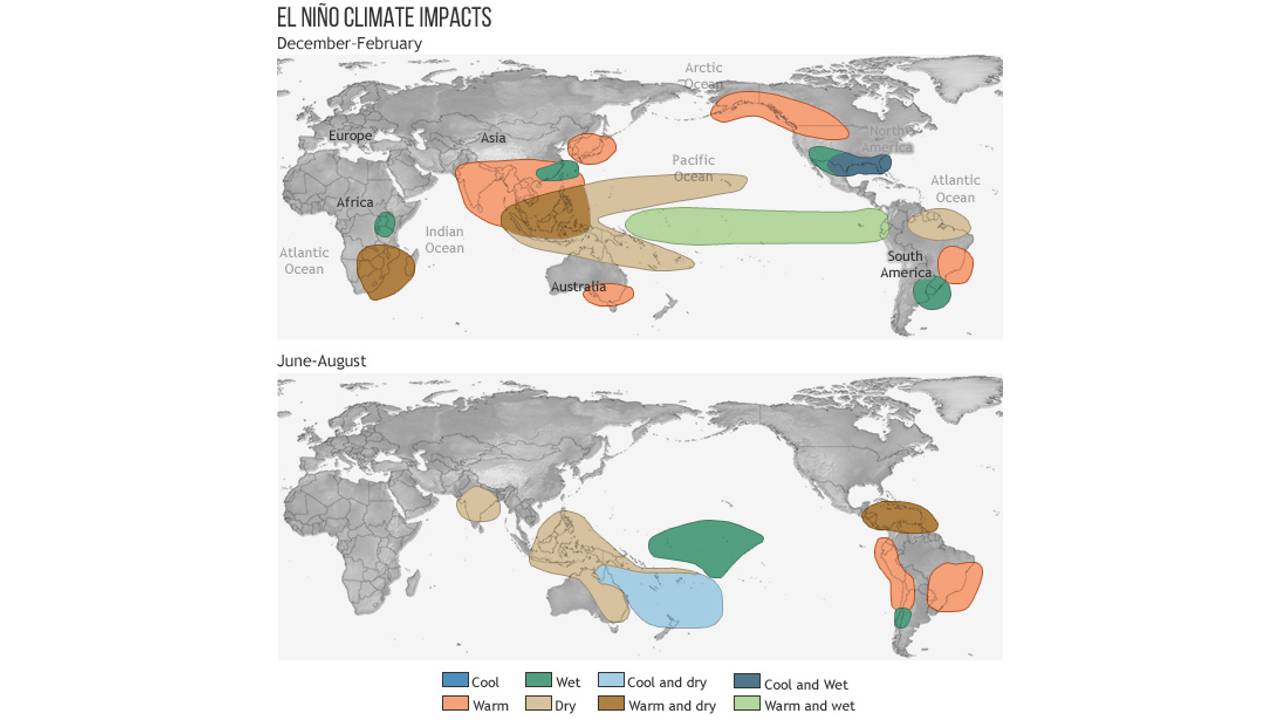
Its strongest climate impacts are usually felt during the Northern Hemisphere’s winter and early spring, bringing more rain and storms across the southern U.S., southeastern South America, the Horn of Africa and eastern Asia. In other parts of the world, such as southeastern Africa and Indonesia, El Niño leads to drier conditions and may increase the risk of drought.
Related: NASA doesn’t know what poked these holes in the Arctic sea ice…
To track El Niño’s progress, scientists measured sea surface temperatures in the east-central tropical Pacific Ocean. Abnormally high temperatures seem to confirm early predictions that this year’s event could be a big one. Atmospheric conditions are also consistent with a long-lasting El Niño, according to NOAA.
“El Niño is a coupled phenomenon, meaning the changes we see in the ocean surface temperatures must be matched by changes in the atmospheric patterns above the tropical Pacific,” the update said. More rain and clouds over the central Pacific, as well as weak pressure in the east and reduced trade wind activity in the west, suggest “the system is engaged and that these conditions will last through the winter,” staff added.
Sea surface temperatures in the east-central tropical Pacific exceeded the long-term average for 1991 to 2020 by 1.8 degrees Fahrenheit (1 degree Celsius) throughout the month of July. Temperatures from May to July — a three-month average called the Oceanic Niño Index — were also 1.4 F (0.8 C) higher than usual and marked the second warmer-than-average Oceanic Niño Index in a row.
“We need to see five consecutive three-month averages above this threshold before these periods will be considered a historical ‘El Niño episode,'” the update said. “Two is a good start.”
There is “a good chance” the Oceanic Niño Index will match or exceed the threshold for a “strong” El Niño, the update added.
And forecasters are now confident the event will remain strong through to next year, although this doesn’t necessarily equate to strong impacts locally, they noted
El Niño affects global weather patterns, as well as the Atlantic and Pacific hurricane seasons. The event usually dampens hurricanes over the Atlantic Ocean, but this year’s sizzling water temperatures could mitigate this dampening effect , according to NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center.
While a hurricane update in May predicted a 30% chance of higher activity over the Atlantic, the latest forecast said there is a 60% chance of an “above normal season,” with up to 21 named storms and five major hurricanes.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.
Note: This article have been indexed to our site. We do not claim legitimacy, ownership or copyright of any of the content above. To see the article at original source Click Here