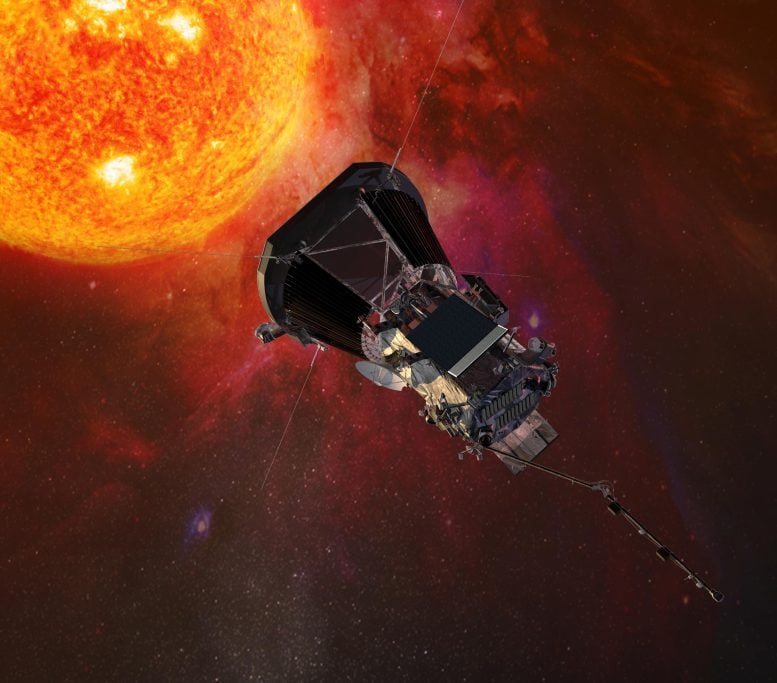
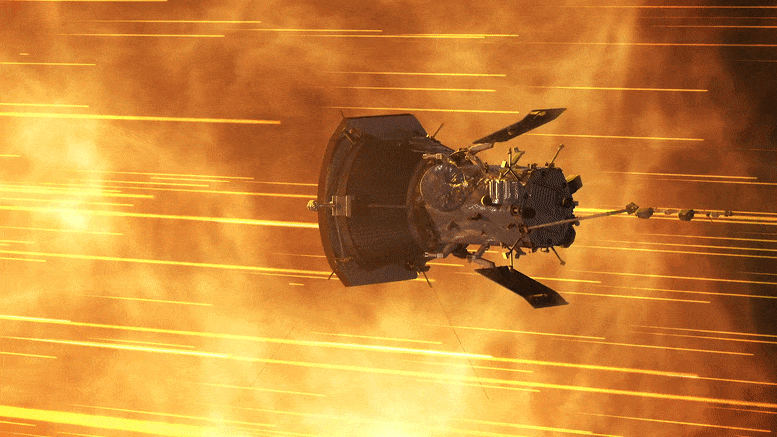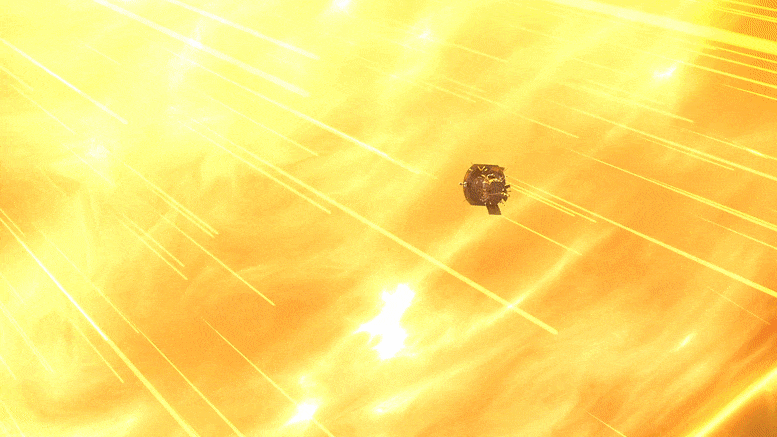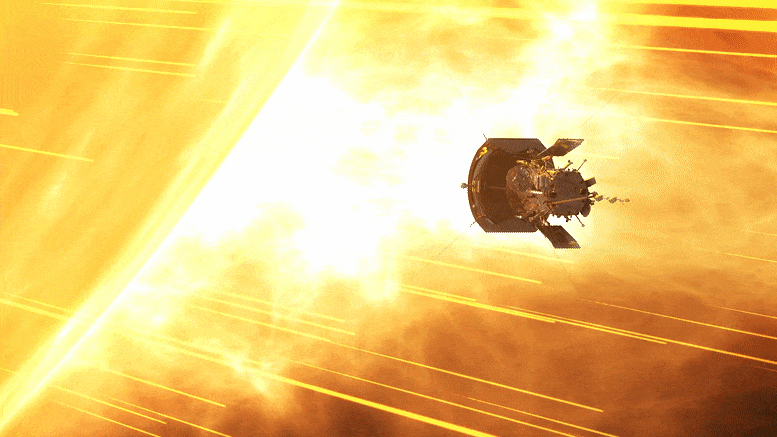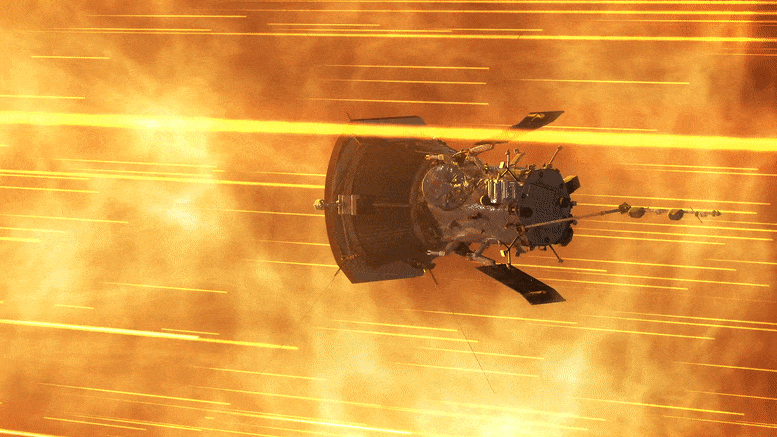
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe successfully completed its 18th close approach to the Sun on December 28, 2023, matching previous distance and speed records, and communicated its healthy status back to mission control. Credit: NASA GSFC/CIL/Brian Monroe
Parker Solar Probe’s 18th close approach to the Sun set distance and speed records, marking a key milestone in its ongoing mission.
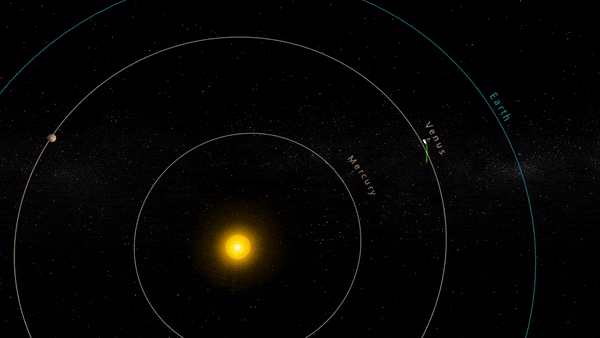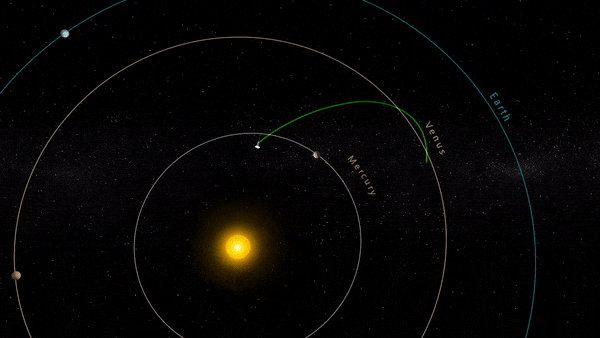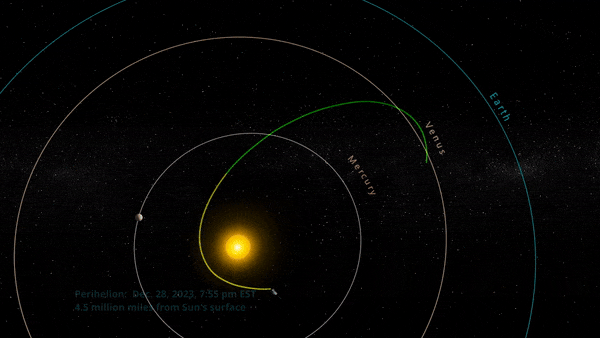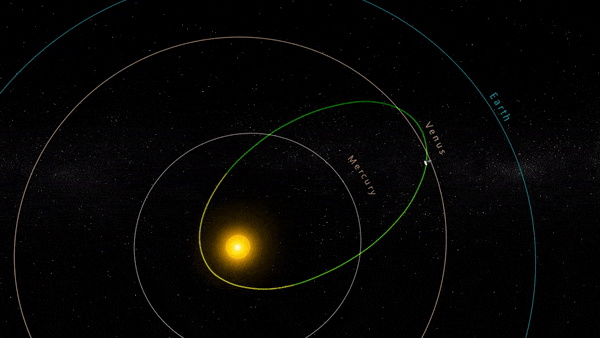
” data-gt-translate-attributes=”[{[{“attribute”:”data-cmtooltip”, “format”:”html”}]” tabindex=”0″ role=”link”>NASA’s Parker Solar Probe completed its 18th close approach to the Sun on December 28, 2023, matching its own distance record by skimming just about 4.51 million miles (7.26 million kilometers) from the solar surface.
The close approach (known as perihelion) occurred at 7:56 p.m. EST, with Parker Solar Probe traveling at 394,736 miles per hour (635,266 kilometers per hour) around the Sun – also matching the speed record for the 17th solar encounter. The milestone also marked the midway point in the mission’s 18th solar encounter, which began December 24, 2023, and continued through January 2, 2024.
Parker Solar Probe’s 18th orbit included a perihelion that brought the spacecraft within 4.51 million miles of the Sun. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins APL/Steve Gribben
The spacecraft entered the encounter in good health, with all systems operating normally. Parker Solar Probe checked back in with mission operators at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland – where the spacecraft was also designed and built – by sending a status beacon tone on January 5.
Illustration of the Parker Solar Probe spacecraft approaching the sun. Credit: Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory
Parker Solar Probe
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe, a groundbreaking mission in solar science, was launched on August 12, 2018, with the primary objective of studying the Sun more closely and in greater detail than any spacecraft before it. Named after solar physicist Eugene Parker, who proposed the existence of the solar wind, this mission marks a significant milestone in humanity’s quest to understand our closest star.
The Parker Solar Probe is designed to withstand extreme heat and radiation near the Sun. It employs a revolutionary heat shield that enables the spacecraft to endure temperatures exceeding 2,500 degrees Fahrenheit while keeping its instruments at a relatively comfortable temperature.
This daring probe aims to unravel the mysteries of the Sun’s corona, the outermost part of the Sun’s atmosphere, which is hotter than its surface for reasons not yet fully understood. The Parker Solar Probe is also tasked with studying solar wind and the mechanisms that accelerate it, along with solar energetic particles, which are crucial for understanding space weather and its impact on Earth.
Throughout its mission, the probe performs a series of close approaches to the Sun, gradually getting closer over time through the use of ” data-gt-translate-attributes=”[{[{“attribute”:”data-cmtooltip”, “format”:”html”}]” tabindex=”0″ role=”link”>Venus’ gravity to alter its orbit. These close encounters provide unprecedented data, offering insights into solar processes that have been puzzling scientists for decades. The success of the Parker Solar Probe is not only a landmark for solar science but also a beacon for future explorations into our solar system and beyond.
Note: This article have been indexed to our site. We do not claim legitimacy, ownership or copyright of any of the content above. To see the article at original source Click Here