Inmarsat Government will provide internet-of-things satellite connectivity for U.S. Army Blue Force Tracker devices
WASHINGTON — Inmarsat Government announced Nov. 7 it won a $410 million, five-year contract extension to provide internet-of-things satellite connectivity for U.S. Army battlefield tracking devices.
The contract, awarded by the Defense Information Systems Agency, is for the Army’s Blue Force Tracker network services.
Inmarsat Government, based in Reston, Virginia, is a subsidiary of British communications satellite operator Inmarsat.
Inmarsat Government will connect the Blue Force Tracker using a new network called ELERA, designed to support IoT services using its existing L-band satellites. This network will provide connectivity between Blue Force Tracker transceivers and satellite ground stations.
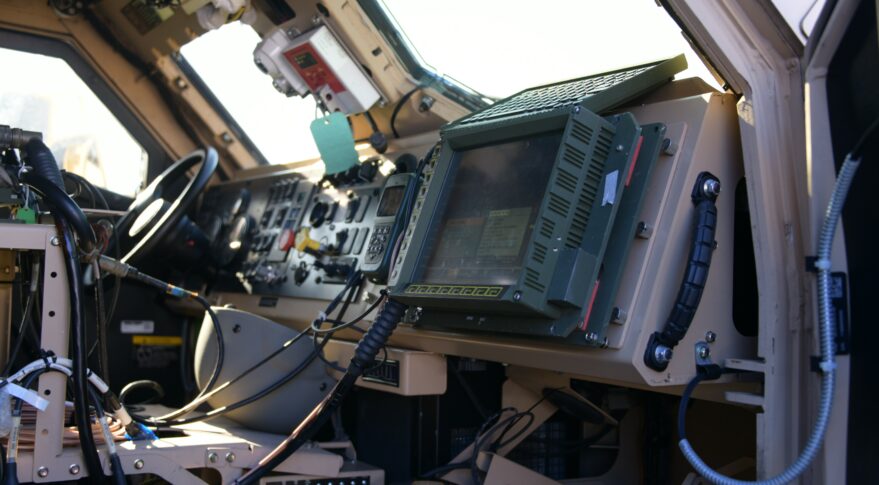
Blue Force tracker devices display friendly force tracking information on tens of thousands of Army platforms.
Inmarsat Government won a previous contract in 2017 to support the Blue Force Tracker network, which has been in operation since 2002. The newest version of Blue Force Tracker has increased network capacity to transfer data, and was designed to be more resilient against electronic warfare attacks.
Note: This article have been indexed to our site. We do not claim legitimacy, ownership or copyright of any of the content above. To see the article at original source Click Here