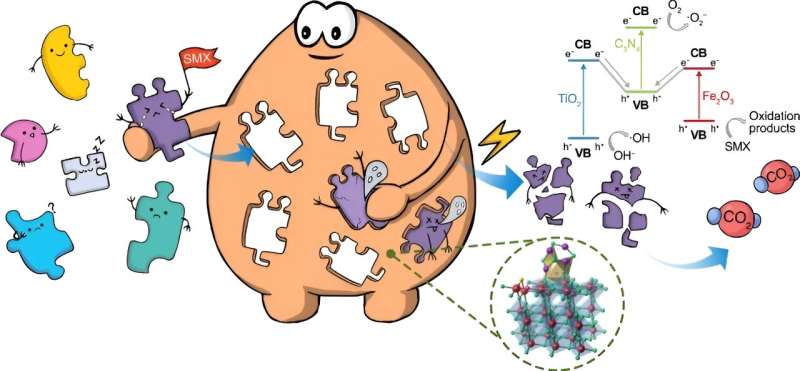
Graphical abstract. Credit: Environmental Science and Ecotechnology (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.ese.2023.100308
In a new study published in Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, researchers from Harbin Institute of Technology, have developed a novel double Z-scheme photocatalyst, called the molecularly imprinted TiO2@Fe2O3@g-C3N4 (MFTC) composite, that selectively removes SMX from water.
Traditional photocatalytic methods have faced challenges with selectivity, often causing the indiscriminate degradation of organic pollutants and coexisting contaminants at high concentrations. However, the MFTC composite was purposefully designed to overcome this limitation by incorporating molecularly imprinted sites on its surface.
These specialized sites exhibit a unique ability to recognize and enhance the adsorption of sulfamethoxazole (SMX), making the MFTC highly effective in selectively targeting SMX in the presence of other pollutants like sulfadiazine (SDZ), ibuprofen (IBU), and bisphenol A (BPA). In simulated wastewater conditions, the MFTC composite impressively demonstrated a selective degradation efficiency rate of 96.8% for SMX, nearly twice as effective as competing catalysts for other pollutants.
The “lock and key” mechanism of the molecularly imprinted sites played a pivotal role in selectively capturing SMX, resulting in superior performance. The degradation process of SMX by the MFTC photocatalytic system involved the generation of •OH and •O2− free radicals, which facilitated the removal of SMX through a newly proposed double Z-scheme mechanism. This mechanism enhanced charge carrier transfer and separation, leading to significantly improved photocatalytic activity.
Moreover, the MFTC composite showcased remarkable stability and recyclability over multiple cycles, making it a promising and practical solution for water treatment applications. The exceptional performance and selectivity of the MFTC composite offer exciting prospects for the advancement of efficient and selective photocatalysts, contributing to the development of eco-friendly and cost-effective solutions for water purification and environmental remediation.
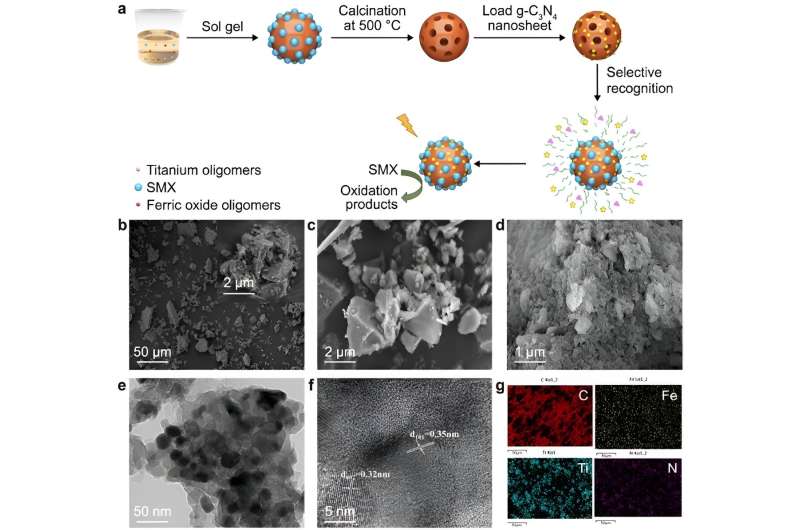
A, The fabrication process of MFTC. b–d, SEM images of MFT (b), NFT (c), MFTC (d). e–f, TEM images of MFTC. g, SEM element mapping images for C, Fe, Ti, and N of MFTC. Credit: Environmental Science and Ecotechnology (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.ese.2023.100308
This research not only provides valuable insights into the selective removal of sulfamethoxazole (SMX) but also opens the door for further exploration of molecularly imprinted nanocomposite materials in selectively eliminating other pharmaceutical residues and organic pollutants.
More information:
Jing-Yan Zhang et al, Selective removal of sulfamethoxazole by a novel double Z-scheme photocatalyst: Preferential recognition and degradation mechanism, Environmental Science and Ecotechnology (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.ese.2023.100308
Provided by
Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences
Citation:
New double z-scheme photocatalyst for selective removal of sulfamethoxazole in water (2023, September 15)
retrieved 5 October 2023
from https://phys.org/news/2023-09-z-scheme-photocatalyst-sulfamethoxazole.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
Note: This article have been indexed to our site. We do not claim legitimacy, ownership or copyright of any of the content above. To see the article at original source Click Here