A new approach to monitoring arachnid behavior could help understand their social dynamics, as well as their habitat’s health.
Andrew Paul
|
Published Apr 2, 2024 10:51 AM EDT
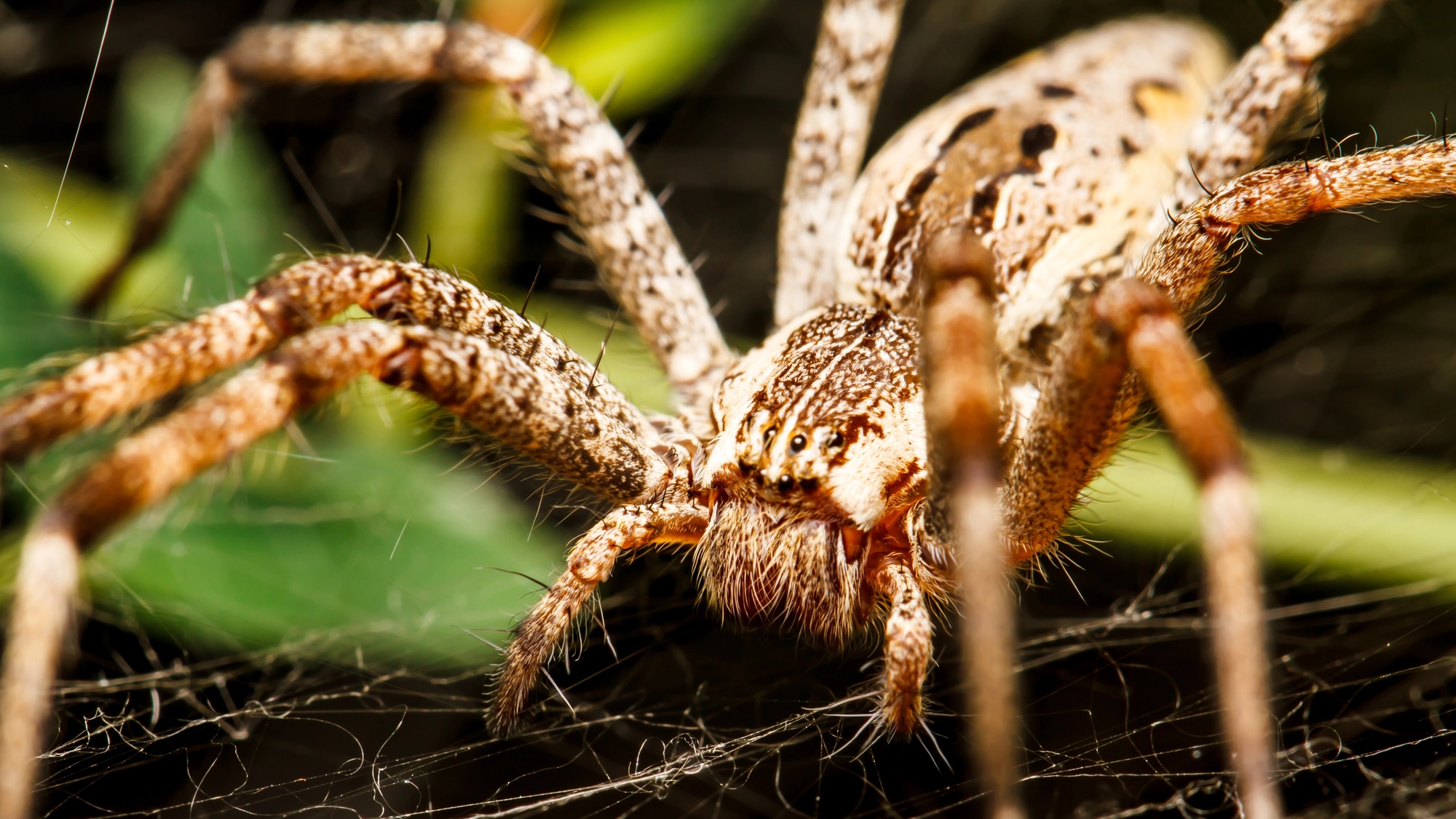

Arachnids are born dancers. After millions of years of evolution, many species rely on fancy footwork to communicate everything from courtship rituals, to territorial disputes, to hunting strategies. Researchers usually observe these movements in lab settings using what are known as laser vibrometers. After aiming the tool’s light beam at a target, the vibrometer measures miniscule vibration frequencies and amplitudes emitted from the Doppler shift effect. Unfortunately, such systems’ cost and sensitivity often limit their field deployment.
To find a solution for this long-standing problem, a University of Nebraska-Lincoln PhD student recently combined an array of tiny, cheap contact microphones alongside a sound-processing machine learning program. Then, once packed up, he headed into the forests of north Mississippi to test out his new system.
Noori Choi’s results, recently published in Communications Biology, highlight a never-before-seen approach to collecting spiders’ extremely hard-to-detect movements across woodland substrates. Choi spent two sweltering summer months placing 25 microphones and pitfall traps across 1,000-square-foot sections of forest floor, then waited for the local wildlife to make its vibratory moves. In the end, Choi left the Magnolia State with 39,000 hours of data including over 17,000 series of vibrations.
[Related:[Related:Meet the first electric blue tarantula known to science.]
Not all those murmurings were the wolf spiders Choi wanted, of course. Forests are loud places filled with active insects, chatty birds, rustling tree branches, as well as the invasive sounds of human life like overhead plane engines. These sound waves are also absorbed into the ground as vibrations, and need to be sifted out from scientists’ arachnid targets.
“The vibroscape is a busier signaling space than we expected, because it includes both airborne and substrate-borne vibrations,” Choi said in a recent university profile.
In the past, this analysis process was a frustratingly tedious, manual endeavor that could severely limit research and dataset scopes. But instead of pouring over roughly 1,625 days’ worth of recordings, Choi designed a machine learning program capable of filtering out unwanted sounds while isolating the vibrations from three separate wolf spider species: Schizocosa stridulans, S. uetzi, and S. duplex.
Further analysis yielded fascinating new insights into arachnid behaviors, particularly an overlap of acoustic frequency, time, and signaling space between the S. stridulans and S. uetzi sibling species. Choi determined that both wolf spider variants usually restricted their signaling for when they were atop leaf litter, not pine debris. According to Choi, this implies that real estate is at a premium for the spiders.
“[They] may have limited options to choose from, because if they choose to signal in different places, on different substrates, they may just disrupt the whole communication and not achieve their goal, like attracting mates,” Choi, now a postdoctoral researcher at Germany’s Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior, said on Monday.
What’s more, S. stridulans and S. uetzi appear to adapt their communication methods depending on how crowded they are at any given time, and who was crowding them. S. stridulans, for example, tended to lengthen their vibration-intense courtship dances when they detected nearby, same-species males. When they sensed nearby S. uetzi, however, they often varied their movements slightly to differentiate them from the other species, thus reducing potential courtship confusion.
In addition to opening up entirely new methods of observing arachnid behavior, Choi’s combination of contact microphones and machine learning analysis could also help others one day monitor an ecosystem’s overall health by keeping an ear on spider populations.
“Even though everyone agrees that arthropods are very important for ecosystem functioning… if they collapse, the whole community can collapse,” Choi said. “Nobody knows how to monitor changes in arthropods.”
Now, however, Choi’s new methodology could allow a non-invasive, accurate, and highly effective aid in staying atop spiders’ daily movements.

Note: This article have been indexed to our site. We do not claim legitimacy, ownership or copyright of any of the content above. To see the article at original source Click Here