Scientists from McGill University develop stronger and tougher glass, inspired by the inner layer of mollusk shells. Instead of shattering upon impact, the new material has the resiliency of plastic and could be used to improve cell phone screens in the future, among other applications.
While techniques like tempering and laminating can help reinforce glass, they are costly and no longer work once the surface is damaged. “Until now there were trade-offs between high strength, toughness, and transparency. Our new material is not only three times stronger than the normal glass, but also more than five times more fracture resistant,” says Allen Ehrlicher, an Associate Professor in the Department of Bioengineering at McGill University.
Nature as master of design
Drawing inspiration from nature, the scientist created a new glass and acrylic composite material that mimics nacre or mother of pearl. “Nature is a master of design. Studying the structure of biological materials and understanding how they work offers inspiration, and sometimes blueprints, for new materials,” says Ehrlicher.
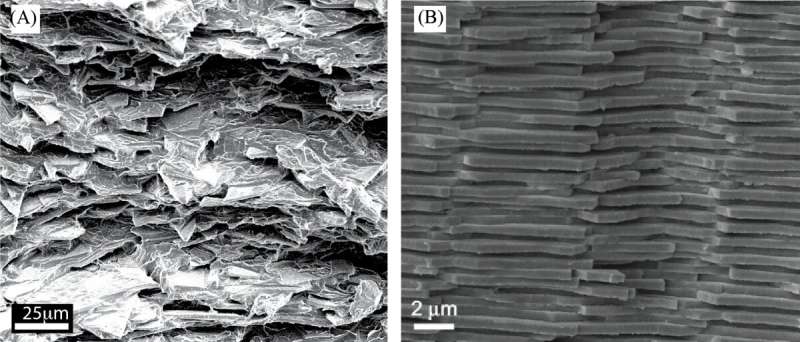
“Amazingly, nacre has the rigidity of a stiff material and durability of a soft material, giving it the best of both worlds,” he explains. “It’s made of stiff pieces of chalk-like matter that are layered with soft proteins that are highly elastic. This structure produces exceptional strength, making it 3000 times tougher than the materials that compose it.”
The scientists took the architecture of nacre and replicated it with layers of glass flakes and acrylic, yielding an exceptionally strong yet opaque material that can be produced easily and inexpensively. They then went a step further to make the composite optically transparent. “By tuning the refractive index of the acrylic, we made it seamlessly blend with the glass to make a truly transparent composite,” says lead author Ali Amini, a Postdoctoral Researcher at McGill. As next steps they plan to improve it by incorporating smart technology allowing the glass to change its properties, such as color, mechanics, and conductivity.
Lost invention of flexible glass
Flexible glass is supposedly a lost invention from the time of the reign of the Roman Emperor Tiberius Caesar. According to popular historical accounts by Roman authors Gaius Plinius Secundus and Petronius, the inventor brought a drinking bowl made of the material before the Emperor. When the bowl was put to the test to break it, it only dented instead of shattering.
After the inventor swore he was the only person who knew how to produce the material, Tiberius had the man executed, fearing that the glass would devalue gold and silver because it might be more valuable.
“When I think about the story of Tiberius, I’m glad that our material innovation leads to publication rather than execution,” says Ehrlicher.
More information: Ali Amini et al, Centrifugation and index matching yield a strong and transparent bioinspired nacreous composite, Science (2021). DOI: 10.1126/science.abf0277
Citation: Unbreakable glass inspired by seashells (2021, September 28) retrieved 2 October 2021 from https://phys.org/news/2021-09-unbreakable-glass-seashells.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
Note: This article have been indexed to our site. We do not claim ownership or copyright of any of the content above. To see the article at original source Click Here












