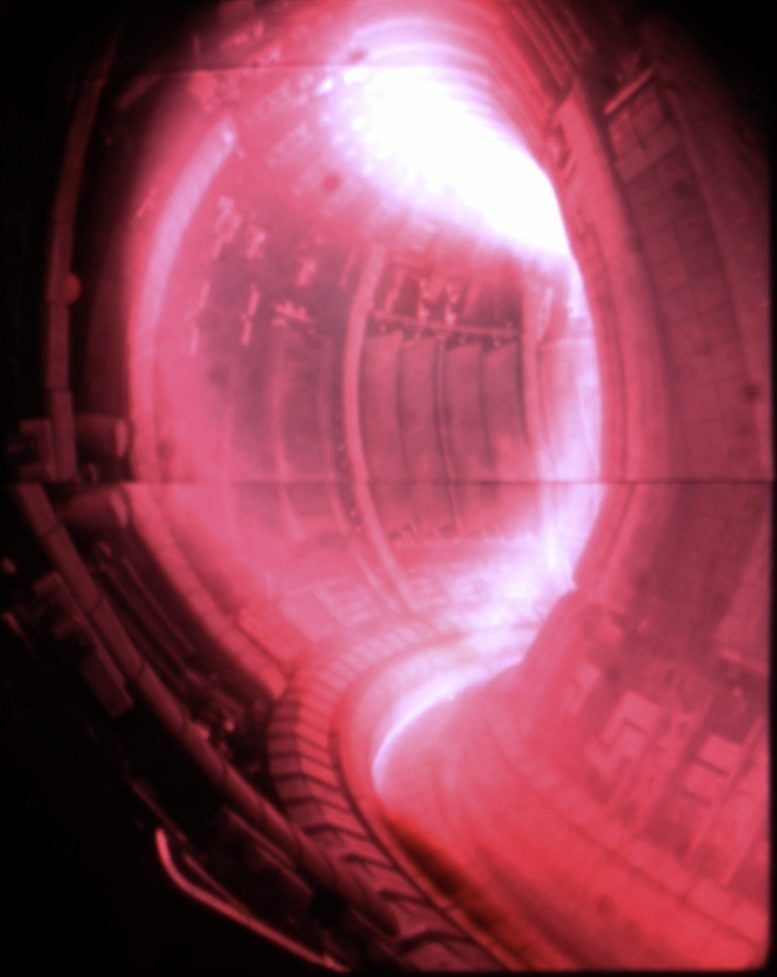
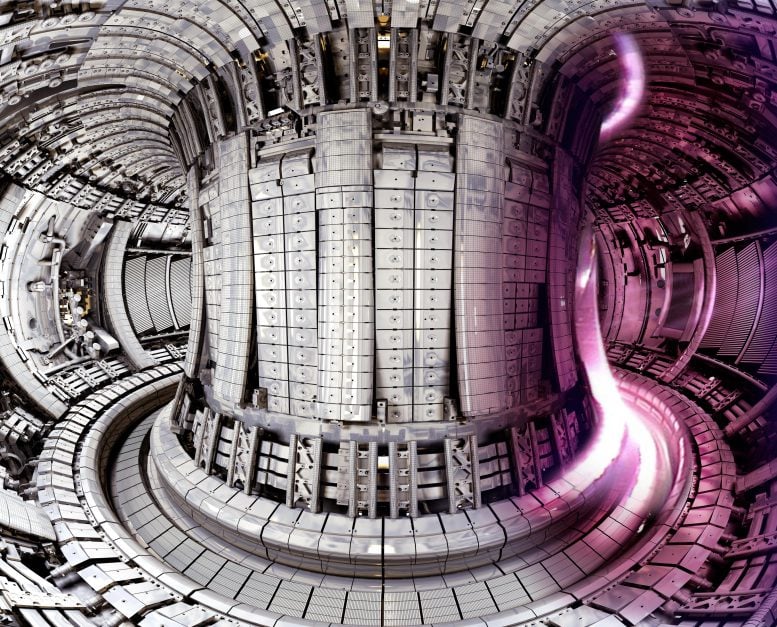
Interior of the Joint European Torus (JET) tokamak experimental fusion machine with a photo of the plasma overlaid. Credit: United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority, courtesy of EUROfusion
The Joint European Torus (JET), one of the world’s largest and most powerful fusion machines, has proven its capability to consistently produce fusion energy and has also established a new world record for energy output.
These notable accomplishments represent a significant milestone in the field of fusion science and engineering.
In JET’s final deuterium-tritium experiments (DTE3), high fusion power was consistently produced for 5 seconds, resulting in a ground-breaking record of 69 megajoules using a mere 0.2 milligrams of fuel.
JET is a tokamak, a design that uses powerful magnetic fields to confine a plasma in the shape of a doughnut. Most approaches to creating commercial fusion favor the use of two hydrogen variants – deuterium and tritium. When deuterium and tritium fuse together they produce helium and vast amounts of energy, a reaction that will form the basis of future fusion powerplants.
Expertise and Future Impact
Dr Fernanda Rimini, JET Senior Exploitation Manager, said: “We can reliably create fusion plasmas using the same fuel mixture to be used by commercial fusion energy powerplants, showcasing the advanced expertise developed over time.”
Professor Ambrogio Fasoli, Programme Manager (CEO) at EUROfusion, said: “Our successful demonstration of operational scenarios for future fusion machines like ITER and DEMO, validated by the new energy record, instill greater confidence in the development of fusion energy. Beyond setting a new record, we achieved things we’ve never done before and deepened our understanding of fusion physics.”
Video inside the Joint European Torus tokamak of pulse #104522 from 3 October 2023, which set a new fusion energy record of 69 megajoules. Credit: United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority, courtesy of EUROfusion
Dr. Emmanuel Joffrin, EUROfusion Tokamak Exploitation Task Force Leader from CEA, said: “Not only did we demonstrate how to soften the intense heat flowing from the plasma to the exhaust, we also showed in JET how we can get the plasma edge into a stable state thus preventing bursts of energy reaching the wall. Both techniques are intended to protect the integrity of the walls of future machines. This is the first time that we’ve ever been able to test those scenarios in a deuterium-tritium environment.”
Global Collaboration and Legacy
Over 300 scientists and engineers from EUROfusion – a consortium of researchers across Europe, contributed to these landmark experiments at the UK Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA) site in Oxford, showcasing the unparalleled dedication and effectiveness of the international team at JET.
The results solidify JET’s pivotal role in advancing safe, low-carbon, and sustainable fusion energy.
Looking inside the Joint European Torus tokamak at pulse #104522 from 3 October 2023, which set a new fusion energy record of 69 megajoules. Credit: United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority, courtesy of EUROfusion
UK Minister for Nuclear and Networks, Andrew Bowie, said: “JET’s final fusion experiment is a fitting swansong after all the groundbreaking work that has gone into the project since 1983. We are closer to fusion energy than ever before thanks to the international team of scientists and engineers in Oxfordshire. The work doesn’t stop here. Our Fusion Futures program has committed £650 million to invest in research and facilities, cementing the UK’s position as a global fusion hub.”
JET concluded its scientific operations at the end of December 2023.
Professor Sir Ian Chapman, UKAEA CEO, said: “JET has operated as close to powerplant conditions as is possible with today’s facilities, and its legacy will be pervasive in all future powerplants. It has a critical role in bringing us closer to a safe and sustainable future.”
JET’s Role in Advancing Fusion Energy
JET’s research findings have critical implications not only for ITER – a fusion research mega-project being built in the south of France – but also for the UK’s STEP prototype powerplant, Europe’s demonstration powerplant, DEMO, and other global fusion projects, pursuing a future of safe, low-carbon, and sustainable energy.
Dr Pietro Barabaschi, ITER Director-General, said: “Throughout its lifecycle, JET has been remarkably helpful as a precursor to ITER: in the testing of new materials, in the development of innovative new components, and nowhere more than in the generation of scientific data from Deuterium-Tritium fusion. The results obtained here will directly and positively impact ITER, validating the way forward and enabling us to progress faster toward our performance goals. On a personal note, it has been a great privilege to have been at JET for a few years. There I had the opportunity to learn from many exceptional people.”
JET has been instrumental in advancing fusion energy for over four decades, symbolizing international scientific collaboration, engineering excellence, and the commitment to harness the power of fusion energy – the same reactions that fuel the Sun and stars.
JET demonstrated sustained fusion over five seconds at high power and set a world record in 2021. JET’s first deuterium-tritium experiments took place in 1997.
As it transitions into the next phase of its life cycle for repurposing and decommissioning, a celebration in late February 2024 will honor its founding vision and the collaborative spirit that has driven its success.
The achievements at JET, from the major scientific milestones to the setting of energy records, underscores the facility’s enduring legacy in the evolution of fusion technology.
Its contributions to fusion science and engineering have played a crucial role in accelerating the development of fusion energy, which promises to be a safe, low carbon, and sustainable part of the world’s future energy supply.
The research was funded by the Euratom Research and Training Programme.
Note: This article have been indexed to our site. We do not claim legitimacy, ownership or copyright of any of the content above. To see the article at original source Click Here