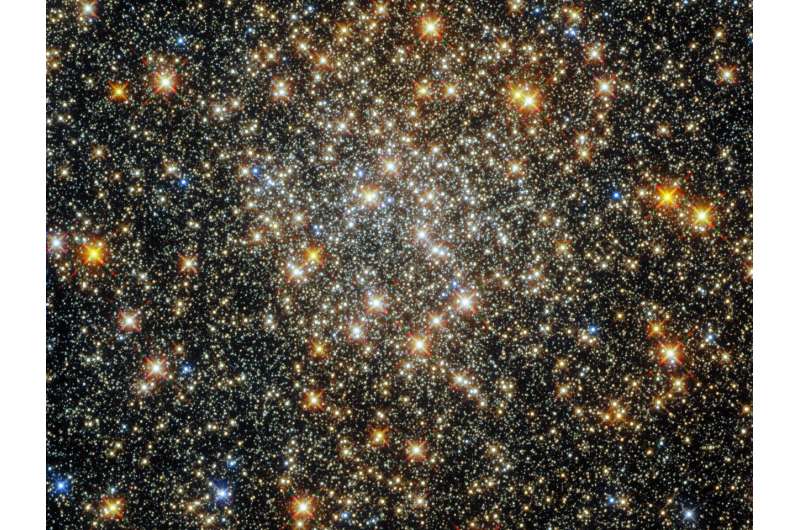
This sparkling starfield, captured by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope’s Wide Field Camera 3 and Advanced Camera for Surveys, contains the globular cluster ESO 520-21 (also known as Palomar 6). A densely packed, roughly spherical collection of stars, it lies close to the center of the Milky Way, where interstellar gas and dust absorb starlight and make observations more challenging.
Interstellar absorption affects some wavelengths of light more than others, changing the colors of astronomical objects by causing them to appear redder than they actually are. Astronomers call this process “reddening,” and it makes determining the properties of globular clusters close to the galactic center—such as ESO 520-21—particularly difficult.
ESO 520-21 lies in the constellation Ophiuchus, near the celestial equator. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations included in the writings of the second-century Egyptian astronomer Ptolemy, all of which are among the 88 constellations officially recognized by the International Astronomical Union today.
Citation: Hubble captures a cluster in the heart of the Milky Way (2021, September 24) retrieved 5 October 2021 from https://phys.org/news/2021-09-hubble-captures-cluster-heart-milky.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
Note: This article have been indexed to our site. We do not claim legitimacy, ownership or copyright of any of the content above. To see the article at original source Click Here