The so-far successful battle this month in California to save the world’s biggest trees from ever-worsening forest blazes seems to offer an important lesson: You can fight fire with fire.
Human-caused climate change has made the western United States hotter, drier and more vulnerable to increasingly destructive wildfires, which have this year taken a horrific toll on the region’s forests.
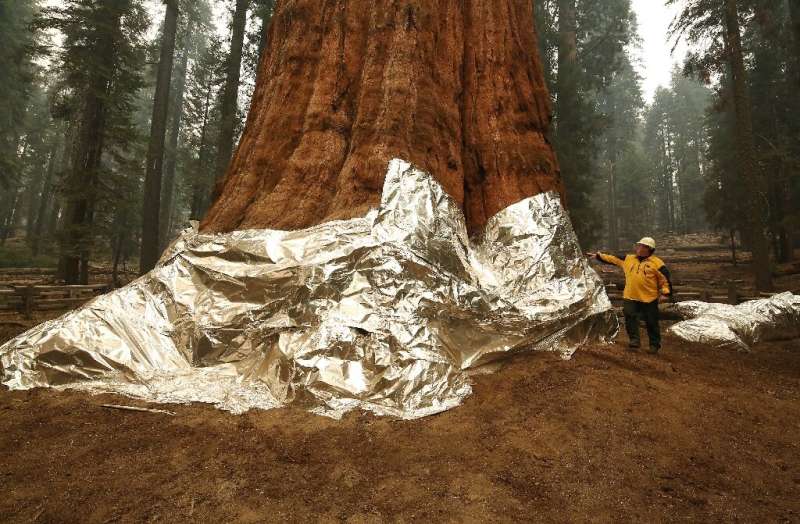
That has included threatening huge sequoias like the General Sherman, which looms 275 feet (83 meters) above the forest floor.
Firefighters were able to beat back the flames as they ate into California’s Giant Forest, thanks to decades of prescribed burns that starved the blaze of fuel.
“It sounds a little strange to say this, but there actually has not been enough fire in California for about a century,” said Rebecca Miller, a researcher at the University of Southern California.
“There were policies in place at the federal and the state level throughout much of the 20th century to prevent fire, because there was an incorrect belief that fire was bad for the environment.”
Fires are part of the natural cycle of forest life, clearing away excess vegetation, purging pests, and making space for new growth.
In the wilderness, these fires eventually burn themselves out.
But as human settlement has encroached further into formerly wild spaces, tolerance for these fires has diminished and firefighters are under instructions to put out all blazes as soon as possible.
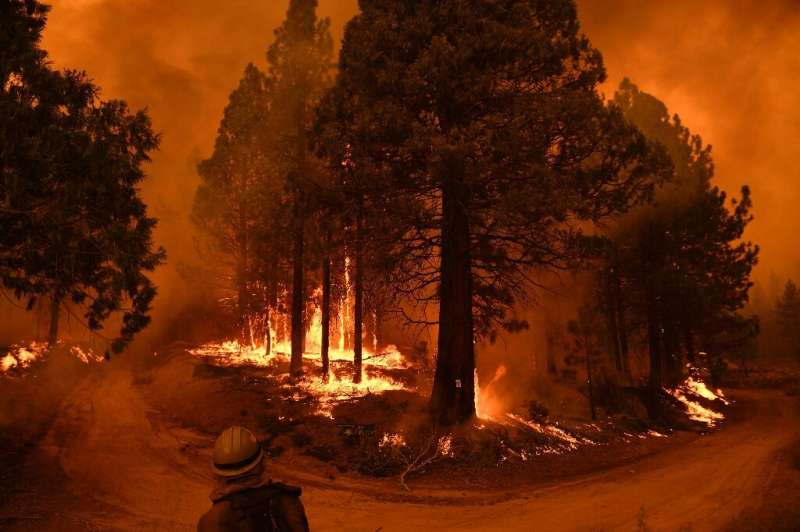

Now there is a growing realization that this policy is actually contributing to the worsening of forest fires—giving them so much more fuel and making them hotter, faster and more destructive.
Instead, the thinking goes, we should actually be helping smaller fires to burn.
The practice was key to protecting Giant Forest, home to the General Sherman, says Mark Garrett, a spokesman for the force trying to tame the still-active KNP Complex fire.
‘Best tool we have’
The sequoias of Giant Forest, some of which are up to 3,000 years old, have survived countless previous fires.
Their thick bark protects them from flames, and their cones actually need the heat of smaller fires to open up and spread their seeds.
But even these imposing giants cannot cope with the mega blazes tearing through California’s parched landscape.
Around 10,000 of them—up to 14 percent of the world’s total—perished in a huge fire last year.
So there was considerable nervousness when flames from the KNP Complex started eating into the Sequoia National Forest.
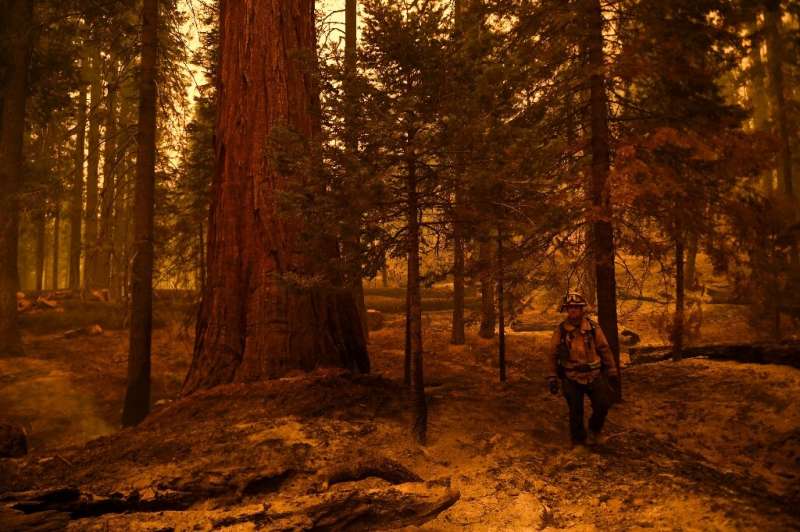

Garrett says it was the first time an uncontrolled fire had come so close to the General Sherman, which was wrapped in a protective foil.
But thanks to years of controlled burns, the fire couldn’t get much of a purchase, said Garrett.
“We’re seeing things we haven’t seen before, like near 300-foot trees being killed because of the smaller trees in between them that are carrying that fire,” he told AFP.
Controlled burns are “the best tool we have right now.”
The next General Sherman
But not everyone agrees.
“It is not an effective strategy and it’s been very much overblown,” says ecologist George Wuerthner.
Controlled burning has to be so widespread and so regular that it’s prohibitive.
“We just can’t be doing the whole landscape at that kind of frequency. It’s misleading to suggest that that’s a panacea for preventing large fires.”
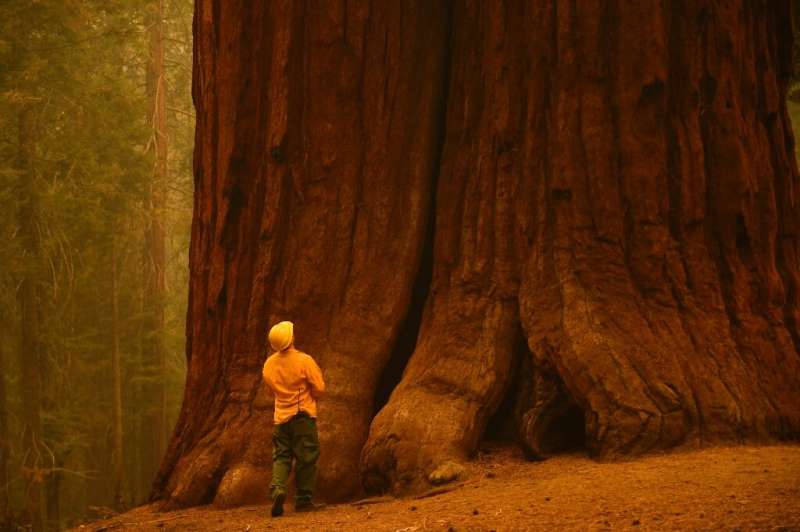

Former forest service official Andy Stahl says worthwhile controlled burns would cost billions of dollars.
“You can’t just burn it, walk away from it and say, ‘Well I don’t have to do that again for another 100 years.”
“No, you have to go back there in another five or 10 years and do it again,” said Stahl, who is executive director of FSEEE, an organization focused on ethical forest management.
Which explains why there are very few areas in the western United States where the practice is common—apart from around Giant Forest.
“It’s a very, very small footprint in a small National Park.”
For Garrett, there is simply no choice: “We need more money. We need more people. This needs to be done, all over the mountains and the federal lands.
“We don’t have a lot of brand new sequoia trees in the Giant Forest because it hasn’t seen fire in so long.
“We need that new generation to replace the General Sherman 2,000 years from now.”
© 2021 AFP
Citation: California fights fire with fire to protect giant sequoias (2021, September 26) retrieved 5 October 2021 from https://phys.org/news/2021-09-california-giant-sequoias.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
Note: This article have been indexed to our site. We do not claim legitimacy, ownership or copyright of any of the content above. To see the article at original source Click Here