The new finding could pave the way for new effective treatments for the coronavirus.
They discovered that the organic compound can bind to many SARS-CoV-2 proteins.
Researchers have discovered that salen can effectively bind a number of proteins of the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. CoV-2’s Scientists utilized molecular docking to reveal that salen binds to the non-structural protein nsp14, which prevents the virus from being destroyed. The discovery may aid in the development of novel drugs and coronavirus infection treatments. The study’s findings were recently published in the journal Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds.
“Our study focused on a well-known compound, salen. We tried to assess the potential activity of this compound against a series of proteins of the SARS-CoV-2, which cause the ” data-gt-translate-attributes=”[{“attribute”:”data-cmtooltip”, “format”:”html”}]”>COVID-19 disease. We found out that salen can potentially interact with the studied proteins, and the best results were obtained for the non-structural protein nsp14, which protects the virus from destruction,” says Damir Safin, Research Engineer at the Organic Synthesis Laboratory of Ural Federal University.
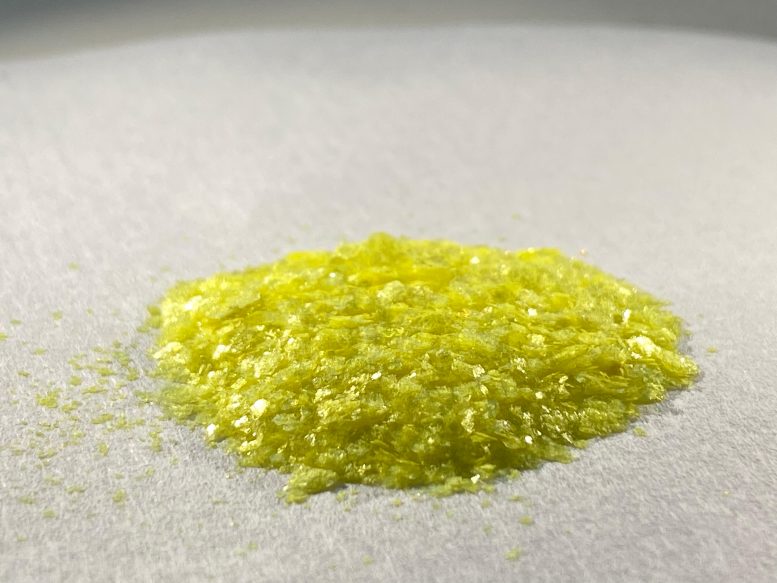
According to scientists, salen – the substance in the photo – is relatively simple and inexpensive to synthesize. Credit: Ural Federal University / Damir Safin
The term “salen” refers to a tetradentate Schiff base derived from salicylaldehyde and ethylenediamine. Salen and its derivatives are key ligands in a wide range of practical applications. This is an organic substance that has the ability to coordinate certain metals and keep them stable in various oxidation states. Metal complex compounds of salen derivatives are also used as catalysts.
Two “fluid” hydrogen atoms of hydroxyl groups are found in salen. Each of these hydrogen atoms has the ability to move to a nitrogen atom, therefore changing the shape of the molecule. This process is known as tautomerization, and the participants are tautomers or tautomeric forms.
“We’ve explored the potential interaction of various tautomers salen with SARS-CoV-2 proteins to identify the most preferred tautomeric form of the studied molecule in terms of the effectiveness in interaction with proteins. Of course, our research is only the first step towards understanding how salen can be used in the fight against COVID-19, much remains to be explored. However, the results we obtained inspire a certain optimism,” adds Damir Safin.
Reference: “Salen: Insight into the Crystal Structure, Hirshfeld Surface Analysis, Optical Properties, DFT, and Molecular Docking Studies” by Maria G. Babashkina, Elizaveta V. Panova, Larisa E. Alkhimova and Damir A. Safin, 22 July 2022, Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds.
DOI: 10.1080/10406638.2022.2097281
A study was carried out by scientists from the Innovation Center of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Technologies of Ural Federal University, Kurgan State University, and Tyumen State University.
Note: This article have been indexed to our site. We do not claim legitimacy, ownership or copyright of any of the content above. To see the article at original source Click Here














