TESTING YOUR LIMITS is an integral part of any training plan, whether you’re performing max pushups or holding a plank. When it comes to strength benchmarks, there are a few classic moves that are typically used to gauge your ability. For your upper body, you might consider how much weight you can bench press. For the large muscles in the lower body, it’s common to use the barbell back squat as your go-to heavyweight exercise.
That leads us to the obvious question: How much should the average guy be able to squat? What if you’re relatively new to lifting, or you aren’t sure when it’s time to add weight to the bar?
First, don’t fixate on how you stack up to the guy next to you at the gym. Everyone’s goals and training history are different. “Volume, intensity, and desired outcome are variables that will impact how much and how often weight should be added to someone’s squat program,” says Kurt Ellis, C.S.C.S., owner and coach at Beyond Numbers Performance.
That said, if you’re curious about where you stand when it comes to squats, here’s what to know, weight ranges to help guide you, and how and when to add more load.
How Much Weight Men Should Be Able to Squat
How much weight you should be able to squat isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer—and that’s a good thing. As with nearly anything in fitness, from goal-setting to recovery plans, your training should be tailored to you. The weight you squat is no different.
“The squat is a very individual-specific lift, meaning that different characteristics of the individual will typically determine how much they’re able to squat,” says Ellis. That means your physical attributes, such as height and torso and limb lengths, can impact how you squat (e.g. whether a wide or narrow stance will be optimal) and also how much you can squat, he explains.
If you’re looking for a general idea of what to aim for overall strength, “men should be able to squat at least 45 percent of their bodyweight” says Ellis, noting that factors such as training age should be taken into consideration. (Don’t forget to factor in how much the barbell weighs on its own.)
If you’ve already surpassed that standard and are looking for a challenge or just want to ensure you’re maintaining strength, “a good bar for most guys would be to work up to squatting your bodyweight,” for a one rep max, says Men’s Health fitness director, Ebenezer Samuel, C.S.C.S. Squats recruit the muscles in your hamstrings, quads, and glutes — all muscles you’ll want to keep strong and healthy as you age and progress in your training, says Samuel.
Back Squat Goals for Every Fitness Level
You may find it more helpful to break down your barbell back squat weight ranges into levels. Taking training age and your current body weight into consideration, Samuel recommends the following goals:
- Beginners (0 to 1 years in the gym): Your bodyweight
- Intermediate (1 to 3 years): 1.25 to 1.5 times your bodyweight
- Advanced (3+ years): 1.75 to twice your bodyweight
How to Safely Increase Your Back Squat Weight
Eager to add another weight plate? These tips can help you increase your strength in the barbell back squat.
Finesse Your Form
If how much weight you’re able to back squat is top of mind for you, then “prioritizing optimal form should be a must,” says Ellis.
As a refresher, here’s how to perform the barbell back squat with proper form:
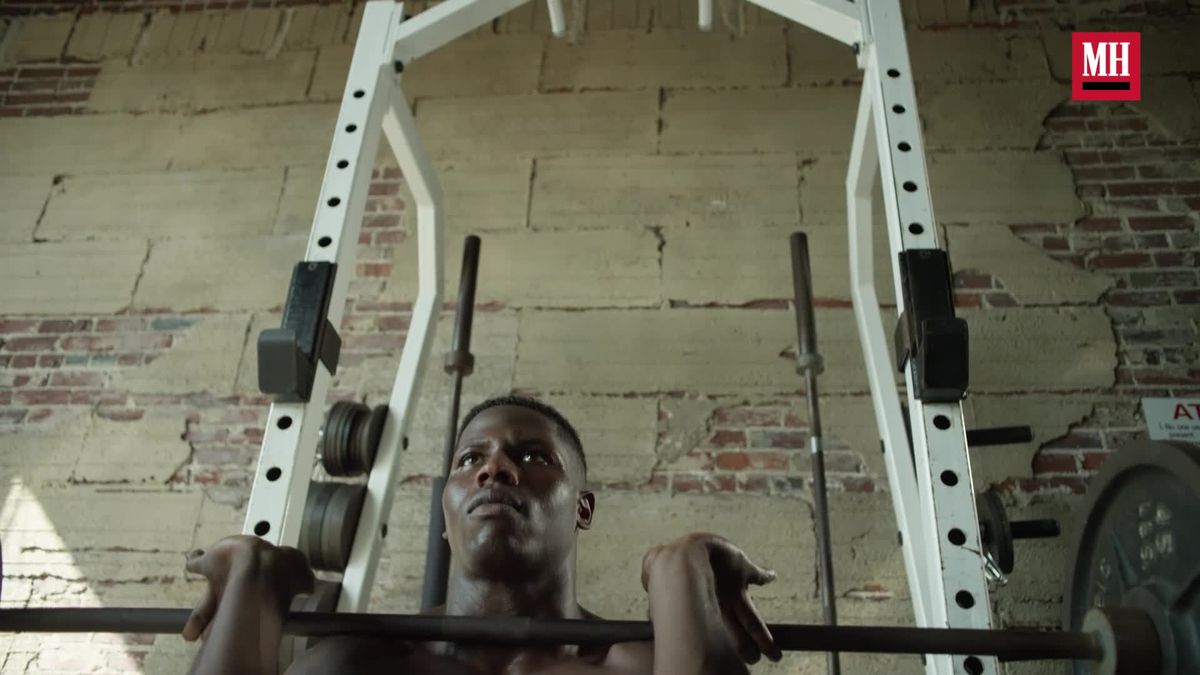

- Dip underneath the bar. Think about creating tension across the shoulder blades as you pull yourself in front of it.
- Place the bar on the meaty portion of your traps—not your neck. Your neck should be able to comfortably stay neutral the whole time. If you feel like you’re craning forward, the bar may be too high.
- Pull the elbows down so that they are almost in line with your torso.
- Push up to get the bar off the hook before stepping back.
- Move the feet so they’re a little wider than shoulder width, with the toes pointed slightly outward.
- Start by pushing the butt back and tilting the torso forward just slightly before you start bending the knees. Take a deep inhale right before you lower. Take your time lowering down—about 2 seconds.
- Open the knees as you lower down. Lower only to the level where you’re able to keep your lower back straight.
- As you push up, raise the torso and hips at the same time. Keep the knees pushed out.
Prioritize Progressive Overload
“Progressive overload is the most straightforward way to improve numbers,” says Ellis. This foundational principle of strength training ensures you’re always, well, progressing by adjusting your training volume, frequency, or intensity in some way.
How can you know if you’re ready to add more weight? Ellis suggests trying what he calls “reps in reserve.” If you’re able to consistently perform three or more additional reps beyond what’s programmed, you’re ready to lift heavier, he says. As for how much to add, don’t go overboard. Ellis recommends incremental increases of no more than 10 percent, so if you’re currently lifting 100 pounds, your next attempt would be 110.
Don’t Neglect Nutrition
“An underrated aspect of improving the numbers on a given lift is the nutrition to match,” says Ellis. You need fuel to expend energy—and you’ll need a lot if you’re pushing to your upper limits of strength.
You can work with a registered dietitian to ensure your eating style sets you up for success in the gym, such as maintaining a good balance of slow-digesting carbs for energy, healthy fats for overall health and immune support, and ample quality protein sources for muscle recovery.
Focus on Recovery
It may be tempting to head straight for the squat rack if you’re hoping to increase your load, but “squatting every day isn’t ideal,” says Ellis. “You need to give the body an opportunity to adapt to the stimuli being presented,” and that happens during rest, he says. While training frequency will depend on the intensity of your workouts and recovery strategies, generally speaking one to three days a week of squatting will work for most people, add Ellis.
Add Accessory Exercises
Yes, you’ll need to actually do the back squat to progress, but you can also program accessory exercises—moves that train the muscles that drive the compound movement—to build strength, too.

Check out these exercises, all of which will help you to build up strength that will pay off when you want to add more plates to your back squat.
Note: This article have been indexed to our site. We do not claim legitimacy, ownership or copyright of any of the content above. To see the article at original source Click Here