A winning combination —
Any mechanical motion deforms the device, such as squishing, stretching, twisting.
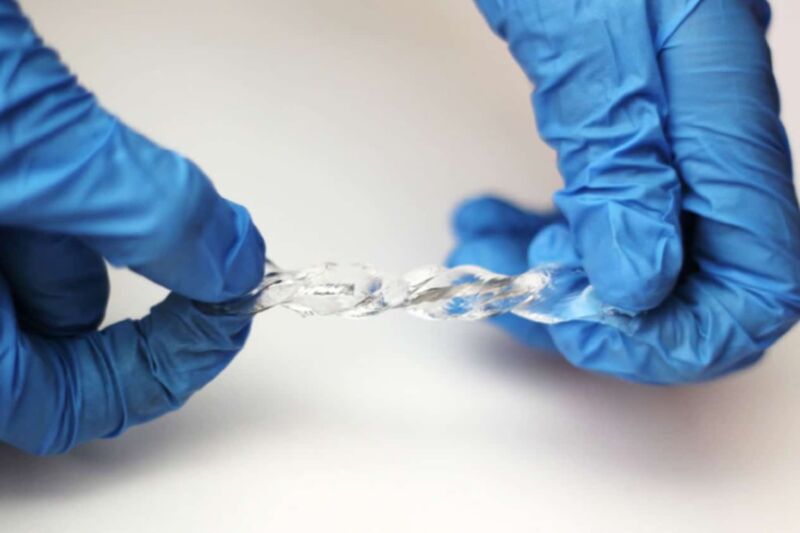

Enlarge / Researchers at North Carolina State University have created a soft and stretchable device that converts movement into electricity. The device works in wet or dry environments and has a host of potential applications.
Scientists at North Carolina State University have developed a flexible, stretchy energy-harvesting device solely out of biocompatible soft materials: liquid metal and soft polymers known as hydrogels. It produces small amounts of electricity comparable to other energy-harvesting technologies, and it can also operate in water as well as air, according to the team’s recent paper published in the journal Advanced Materials. The team thinks the new NCSU device holds promise for powering wearable devices, charging them spontaneously with no need for an external power source.
“Mechanical energy—such as the kinetic energy of wind, waves, body movement and vibrations from motors—is abundant,” said co-author Michael Dickey, a chemical and bimolecular engineer at NCSU. “We have created a device that can turn this type of mechanical motion into electricity. And one of its remarkable attributes is that it works perfectly well underwater.”
The NCSU scientists were particularly inspired by a 2013 paper by Korean researchers. The 2013 researchers found they could harvest energy from an electrical double-layer capacitor (ELCD) by depressing arrays of water droplets sandwiched between two rigid electrodes, thereby spontaneously charging the capacitor. But the rigidity proved to be a shortcoming, since electricity was only generated by moving the stiff electrode up and down. Dickey and his co-authors wanted to create a flexible version of this technology.
The key proved to be a liquid-metal alloy of gallium and indium, per Dickey, which is then encased in a water-absorbent hydrogel. The dissolved salts in the water (ions) congregate on the metallic surface, forming an electrical double layer akin to a capacitor. Deforming the liquid metal increases the area, and the greater the surface area, the greater the induced charge. When electricity is generated, it can be harnessed by an attached wire.
“Since the device is soft, any mechanical motion can cause it to deform, including squishing, stretching, and twisting,” said Dickey. “This makes it versatile for harvesting mechanical energy. For example, the hydrogel is elastic enough to be stretched to five times its original length.”
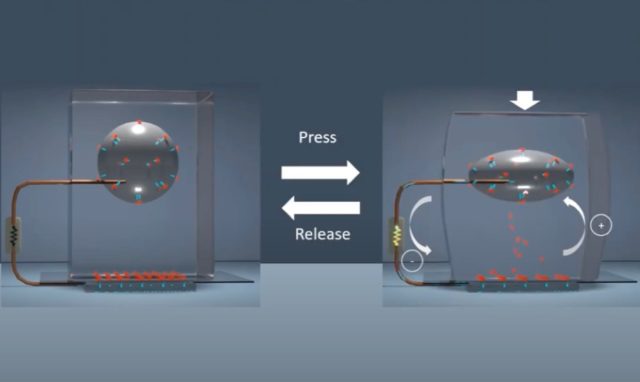
Enlarge / Deforming the device generates current.
YouTube/NCSU
Dickey et al. next tested the energy-harvesting capabilities of their device by deforming one of the electrodes and comparing the results to the other, nondeformed electrode. They found that a deformation of just a few millimeters could generate a power density of about 0.5 mW m-2, which is comparable to other popular energy-harvesting devices.
But the device has one big advantage over its competitors: those competitors typically don’t function well, if at all, in wet environments. This opens up more potential applications, according to Dickey, including biomedicine, athletic clothing, soft robots, e-skins, and uses in marine environments. Their device is also remarkably easy to manufacture in just a few simple steps.
The NCSU researchers used their technology to create a stretchable self-powered sensor capable of sensing the motion of a finger. “Increasing the bending angle of the finger increases the deformation, resulting in an increased current,” they wrote. The sensor could also harvest energy from the motion of the elbow and knee while walking.
There are some potential issues, however. The water in the hydrogel tends to evaporate over time, which would impact its stretchiness and alter its conductivity. This could be mitigated, however, by incorporating lithium-chloride salts into the device. Gallium also tends to oxidize over time, and the researchers did note a decrease in energy potential after several thousand cycles. This could result in lower power outputs over a longer time period. And there is still some energy wasted in the deformation of the hydrogel; even softer gels could possibly improve its energy-conversion efficiency.
The new NCSU device is primarily a proof of concept, according to Dickey. They are also investigating how to adapt their technology to harvest power from wind and ocean waves. And Dickey and his team think they can find a way to further increase the power density of their device.
One way to do this might be by breaking the metal into smaller droplets, essentially increasing the area for a given volume. Alternatively, one might prestretch the device and then let it relax, increasing the electric current (and thus the instantaneous peak power). Or one could precharge the capacitors to increase power output. Finally, “In principle, one might explore other materials, such as ionic liquids or battery electrolytes to extend the operating potential,” the authors concluded.
DOI: Advanced Materials, 2021. 10.1002/adma.202103142 (About DOIs).
Researchers at NC State University report a way to convert mechanical energy into electricity.
Note: This article have been indexed to our site. We do not claim ownership or copyright of any of the content above. To see the article at original source Click Here