Credit: Eco-Environment & Health (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.eehl.2023.11.001
In a study published in the journal Eco-Environment & Health, researchers from Zhejiang University revealed the crucial role of epidermal microorganisms in influencing earthworm toxicity under environmental stress, notably in conditions of nano zero-valent iron (nZVI) and tris (2-chloroethyl) phosphate (TCEP) co-contaminated soil.
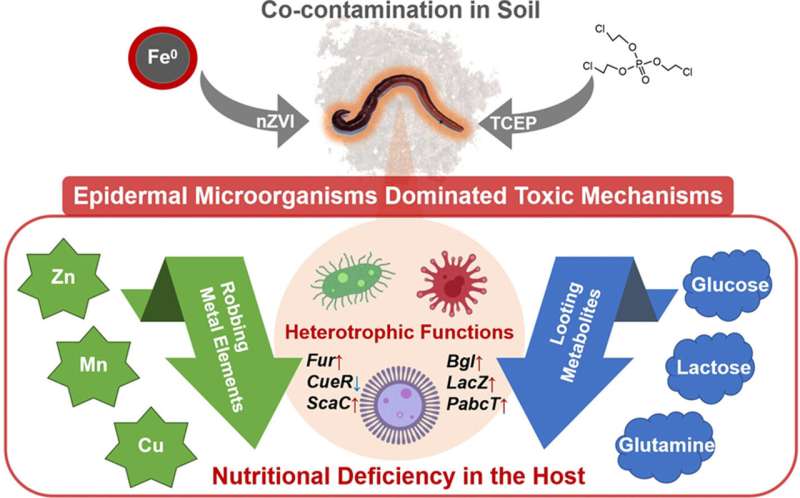
They compared intestinal and epidermal microorganisms’ contributions to earthworm toxicity under single and combined soil contamination scenarios. Using 16S rRNA sequencing and metagenomic analysis techniques, the study observed that 45% of epidermal microbes were highly correlated with host toxicity, in contrast to only 15% of intestinal microbes.
Functional analysis revealed that key epidermal microbes, mainly heterotrophic, had genetic capabilities to utilize metal elements and nutrients. In co-contaminated environments with nZVI and TCEP, certain epidermal microorganisms became dominant, consuming vital elements like zinc, copper, manganese, saccharides, and amino acids. This consumption contributed to nutritional deficiencies in the host earthworms.
Prof. Daohui Lin, lead researcher of the study, stated, “Our findings open a new dimension in understanding host–microbiome–environment interactions. The epidermal microbiome, often overlooked, is crucial in determining an organism’s resistance to environmental pollutants. This could redefine our approach to pollution impact studies and conservation strategies.”
This study sheds light on the previously overlooked role of epidermal microbes in earthworm health and their potential involvement in pollution-related toxicity. It emphasizes the need for a more holistic understanding of the complex interactions between hosts, their symbiotic microorganisms, and environmental contaminants.
Further research is needed to explore the specific mechanisms by which epidermal microbes influence host health and to develop strategies for protecting both the host and its microbial partners from environmental threats.
More information:
Jie Hou et al, Epidermal microorganisms contributed to the toxic mechanism of nZVI and TCEP in earthworms by robbing metal elements and nutrients, Eco-Environment & Health (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.eehl.2023.11.001
Provided by
TranSpread
Citation:
New study reveals impact of skin microorganisms on earthworm toxicity in polluted environments (2024, January 18)
retrieved 10 February 2024
from https://phys.org/news/2024-01-reveals-impact-skin-microorganisms-earthworm.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
Note: This article have been indexed to our site. We do not claim legitimacy, ownership or copyright of any of the content above. To see the article at original source Click Here













